03.06.2018
Elasticsearch and Spring Boot
This article describes how to extend an existing Spring Boot application with a search functionality using Elasticsearch. In the example, one local node is operated and an installation of Elasticsearch is not necessary.
If a Spring Boot application should be equipped with a powerful search functionality, then this variant is one way to achieve that. For example, a fuzzy search is possible and the use of the query DSL makes it easy to implement complex search queries.
Here is an example of an existing Spring Boot application that manages objects of type Item. An item has an id, a description and a place where it is located.
It shows how an item can be found with a part of the description and the storage location.
In general, the extension described here works in such a way that the search arrives at the Spring Boot application via the REST controller. Afterwards, a search is executed using the SearchQueryBuilder and the items are exported from the Elasticsearch node and returned to the caller.
At the start of the application the migrator (ItemMigration) exports all items from the relational database and stores them in the Elasticsearch node.
Configuration
First, create a configuration that defines the repositories (EnableElasticsearchRepositories, EnableJpaRepositories). In addition, the local Elasticsearch node is configured.
package org.hameister.elastic;
import org.elasticsearch.common.settings.Settings;
import org.elasticsearch.node.NodeBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.ElasticsearchOperations;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.ElasticsearchTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.repository.config.EnableElasticsearchRepositories;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.config.EnableJpaRepositories;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
@Configuration
@EnableElasticsearchRepositories(basePackages = "org.hameister.elastic")
@EnableJpaRepositories(basePackages = "org.hameister.repository")
public class ElasticConfiguration {
@Bean
public NodeBuilder nodeBuilder() {
return new NodeBuilder();
}
@Bean
public ElasticsearchTemplate elasticsearchTemplate() throws IOException {
File tmpDir = new File(String.valueOf(System.currentTimeMillis()));
Settings.Builder elasticsearchSettings =
Settings.settingsBuilder()
.put("http.enabled", "true")
.put("index.number_of_shards", "1")
.put("path.data", new File(tmpDir, "data").getAbsolutePath())
.put("path.logs", new File(tmpDir, "logs").getAbsolutePath())
.put("path.work", new File(tmpDir, "work").getAbsolutePath())
.put("path.home", tmpDir);
ElasticsearchTemplate elasticsearchTemplate = new ElasticsearchTemplate(nodeBuilder()
.local(true)
.settings(elasticsearchSettings.build())
.node()
.client());
return elasticsearchTemplate;
}
}
Datamodel
The domain class used for the relational database, in line 14 can you can add the annotation @Document so that Elasticsearch can handle items. Also the index name Item and type is set there.
package org.hameister.model;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnore;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.annotations.Document;
import javax.persistence.*;
import java.time.LocalDate;
/**
* Created by hameister on 24.12.16.
*/
@Entity
@Table(name = "Item")
@Document(indexName = "items", type = "items", shards = 1)
public class Item {
public Item() {
}
public Item(String description, String location, LocalDate itemdate) {
this.description = description;
this.location = location;
this.itemdate = itemdate;
}
public Item(Long id,String description, String location, LocalDate itemdate) {
this.id=id;
this.description = description;
this.location = location;
this.itemdate = itemdate;
}
@Id
@GeneratedValue
Long id;
@Column(name = "description")
private String description;
@Column(name = "location")
private String location;
@JsonIgnore
@Column(name = "itemdate")
private LocalDate itemdate;
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public void setDescription(String description) {
this.description = description;
}
public String getLocation() {
return location;
}
public void setLocation(String location) {
this.location = location;
}
public LocalDate getItemdate() {
return itemdate;
}
public void setItemdate(LocalDate itemdate) {
this.itemdate = itemdate;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
}
Controller
The controller defines the new REST endpoint, which can be reached at /item/elastic. In addition, the incoming request is forwarded to the SearchQueryBuilder, which performs the search in the Elasticsearch node.
package org.hameister.elastic;
import org.hameister.model.Item;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Created by hameister on 26.05.18.
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/item/elastic")
public class ElasticItemController {
@Autowired
private SearchQueryBuilder searchQueryBuilder;
@GetMapping(value = "/{text}")
public List<Item> getAll(@PathVariable final String text) {
try {
return searchQueryBuilder.getAll(text);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
}
Query
In the class SearchQueryBuilder the search for the items is defined. The example uses only the description and location for the search. It is also possible to use the entire query DSL to expand the search.
package org.hameister.elastic;
import org.elasticsearch.index.query.QueryBuilder;
import org.elasticsearch.index.query.QueryBuilders;
import org.hameister.model.Item;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.ElasticsearchTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.query.NativeSearchQuery;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.query.NativeSearchQueryBuilder;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;
@Component
public class SearchQueryBuilder {
private ElasticsearchTemplate elasticsearchTemplate;
@Autowired
public SearchQueryBuilder(ElasticsearchTemplate elasticsearchTemplate) {
this.elasticsearchTemplate = elasticsearchTemplate;
}
/*
Query in Json format. Only description ans location are used for the search.
SEARCHTEXT is can be for example: 'Tas Reg'
This SEARCHTEXT will find all Tassen in Regals.
{
"bool" : {
"should" : [ {
"query_string" : {
"query" : "SEARCHTEXT",
"fields" : [ "description", "location" ],
"lenient" : true
}
}, {
"query_string" : {
"query" : "*SEARCHTEXT*",
"fields" : [ "description", "location" ],
"lenient" : true
}
} ]
}
}
*/
public List<Item> getAll(String text) throws IOException {
QueryBuilder query = QueryBuilders.boolQuery()
.should(
QueryBuilders.queryStringQuery(text)
.lenient(true)
.field("description")
.field("location")
).should(QueryBuilders.queryStringQuery("*" + text + "*")
.lenient(true)
.field("description")
.field("location"));
NativeSearchQuery build = new NativeSearchQueryBuilder()
.withQuery(query)
.build();
return elasticsearchTemplate.queryForList(build, Item.class);
}
}
Migrator
Finally, the class ItemMigrator is used to export the complete data from the relational database when the application is started and stores it in the Elasticsearch node.
package org.hameister.elastic;
import org.hameister.model.Item;
import org.hameister.elastic.ElasticItemRepository;
import org.hameister.repository.ItemRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener;
import org.springframework.context.event.ContextRefreshedEvent;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.ElasticsearchOperations;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.ElasticsearchTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import java.time.LocalDate;
/**
* Created by hameister on 26.05.18.
*/
@Component
public class ItemMigrator {
ElasticsearchOperations operations;
ElasticItemRepository elasticUsersRepository;
ItemRepository repository;
@Autowired
public ItemMigrator(ItemRepository jpaRepository, ElasticsearchTemplate operations, ElasticItemRepository elasticUsersRepository) {
this.repository = jpaRepository;
this.operations = operations;
this.elasticUsersRepository = elasticUsersRepository;
}
@PostConstruct
@Transactional
public void loadAll() {
Iterable<Item> items = repository.findAll();
operations.putMapping(Item.class);
elasticUsersRepository.save(items);
}
}
Notes: In a productively used application not only a local node should be used, but at least one Elasticsearch instance. Besides, the data should not have to be exported completely from the relations database every time. It should be noted that with Spring Boot 1.5 the two repositories can not be in the same package, otherwise the component scan will not work. This issue should be resolved with Spring Boot 2.0.
The complete source code can be found in the Github repository at the following url https://github.com/hameister/ItemStore. The extensions are in the branch elastic.
The following screenshot shows how to call the REST endpoint with Postman, for example, to search for cups Tas for Tasse on shelves Reg for Regal.
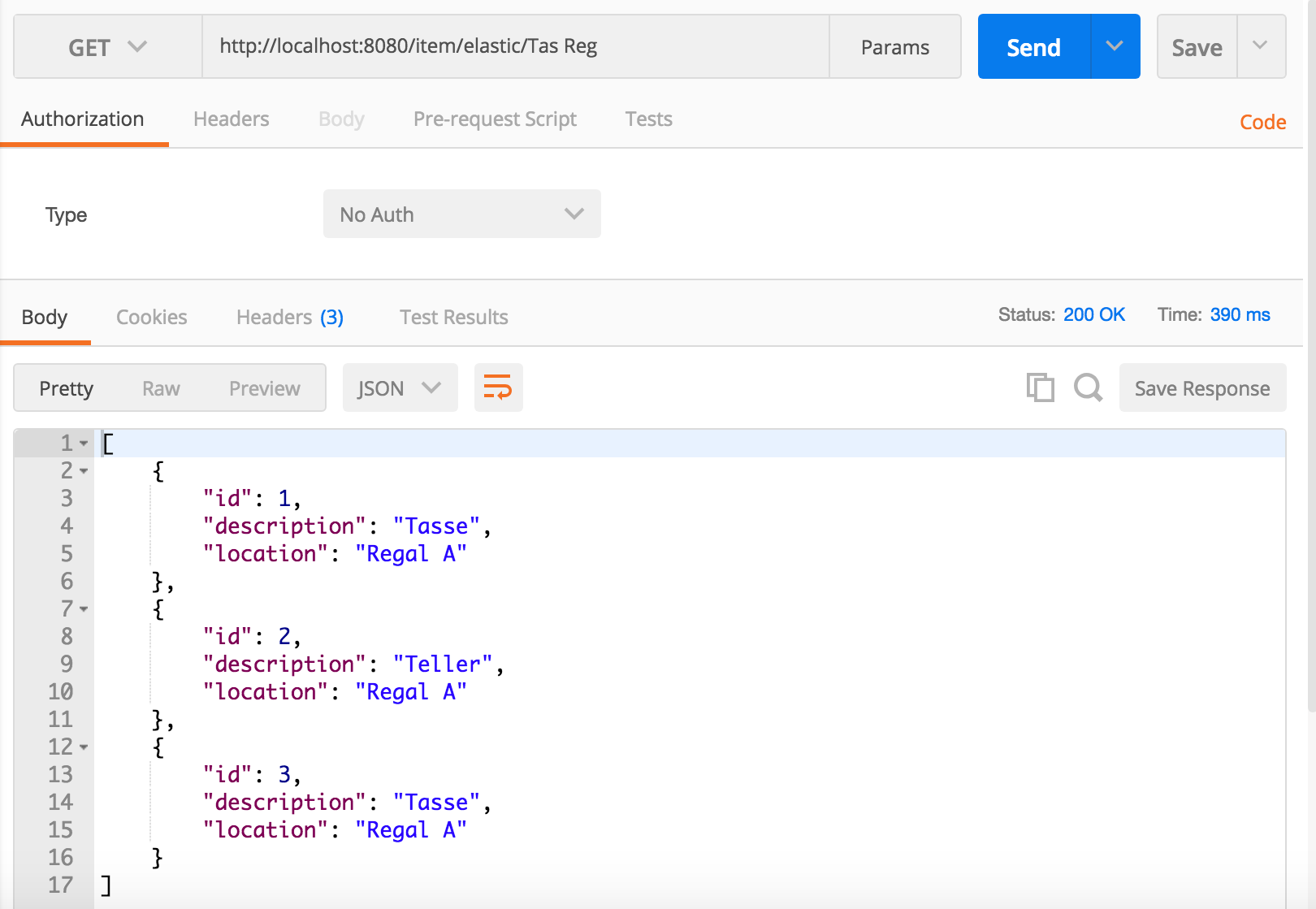
If you want to call the endpoint with the browser, it works with the following URL: http://localhost:8080/item/elastic/Tas%20Reg

